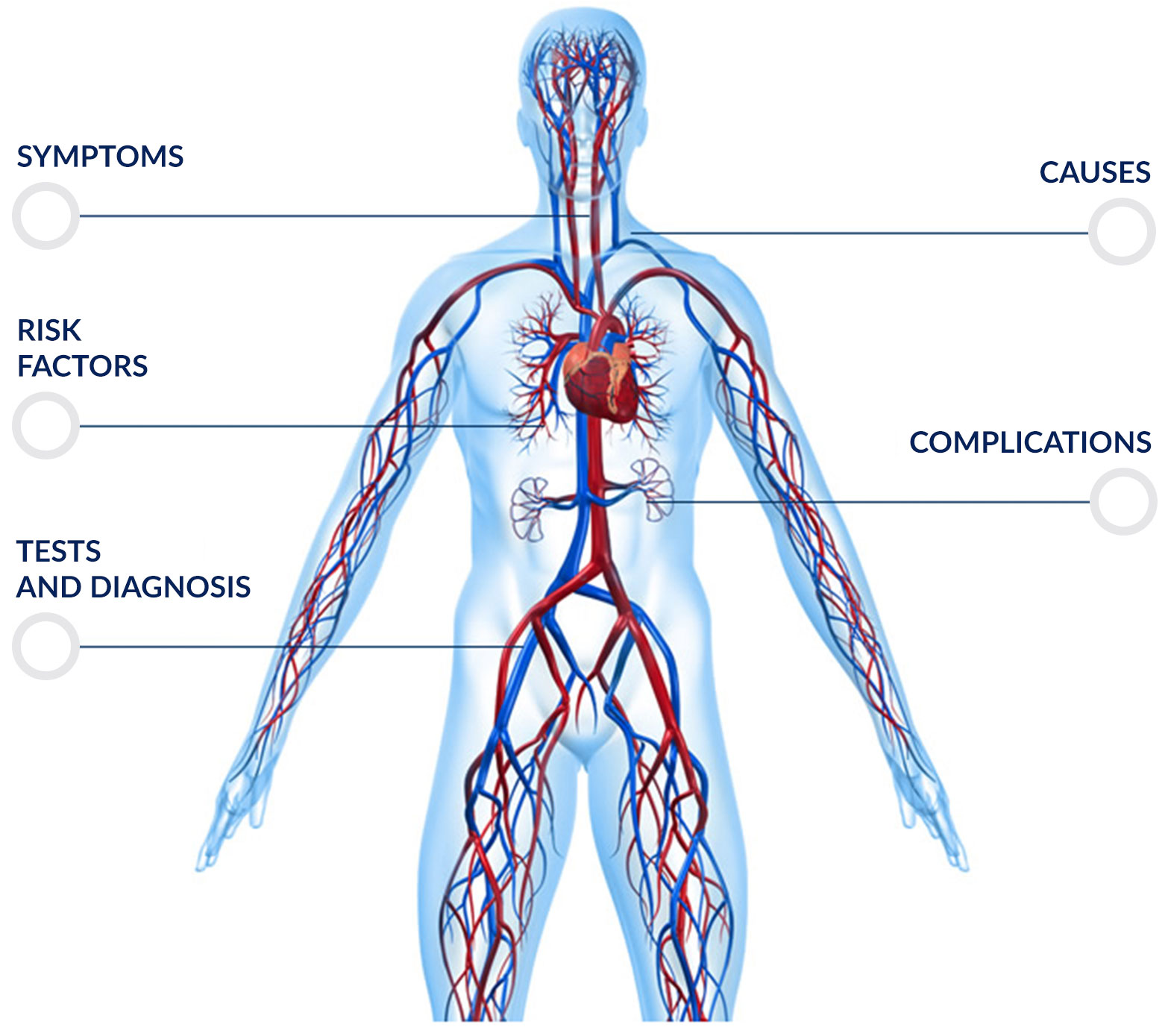
Cholesterol is an organic compound belonging to the family of lipids. It performs various biological functions in the body, which are important and essential to build healthy cells, for the production of certain hormones, vitamin D and bile salts. In spite of its essential biologic function, when cholesterol circulates in the blood in concentrations that are higher than normal (hypercholesterolemia), it becomes a hazard for health, increasing the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
Hypercholesterolemia can lead to the formation of pathological fat deposits in blood vessels. This may affect the smooth flow of blood in vessels that supply both the heart and the brain, thus causing a risk of either acute or chronic ischemic attacks or causing strokes.
Hypercholesterolemia, which can be hereditary, is often the result of unhealthy life choices and, as such, it can be prevented and treated. A healthy diet, regular physical exercise and, associated pharmaceutical treatment upon indication of a medical professional may result in significant long-term reduction or prevention of the disease.
Select to learn more